
When selecting a CNC machining center, one critical decision is choosing between ball guides and roller guides for the linear motion system. Both types belong to the linear guideway family but differ significantly in design, performance, and application. This article clarifies their distinctions to help you make an informed choice.
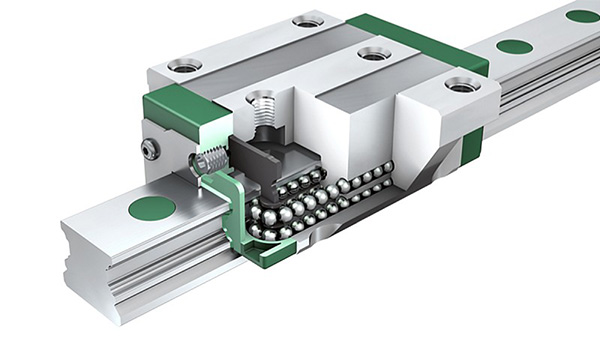
What is Linear Ball Guide?
Linear Ball Guide is a precision linear motion system that utilizes steel balls as rolling elements mounted in a carriage that slides along a hardened steel rail. Their point contact design greatly reduces friction, enabling high speeds (up to 100 m/min) while maintaining the extremely high positional accuracy that is essential for machining complex components such as smartphone housings, medical devices or glass engraving. However, this type of contact limits their load-carrying capacity compared to roller systems, as prolonged heavy loads cause deformation (“ovalization”) of the steel balls, which gradually affects accuracy.
These guides excel in lightweight material processing (e.g., aluminum alloys, plastics) applications in industries such as consumer electronics, aerospace prototyping, and mold making. Common brand types include: THK BGC series, HIWIN BGL series and NSK LB series. Roller guides may be the preferred choice for demanding continuous tasks, but ball guides are still the preferred choice for applications requiring fast, nano-scale precision.
What is Linear Roller Guide?
Roller Linear Rail is an advanced linear motion system that provides excellent strength and stability through the use of cylindrical rollers rather than traditional steel balls. These rollers are arranged in flat rows and columns or in innovative crossover configurations, such as crossed roller guides, to ensure linear contact with the rail surface. This design distributes loads evenly over a larger contact area than point contact ball guides, resulting in superior stiffness, reduced stress concentrations and increased resistance to fatigue from gravity or repetitive forces.
Key benefits include ultra-high stiffness, making it ideal for demanding applications such as deep groove milling of automotive or aerospace components. Their robust construction also ensures long service life in harsh environments due to the large contact area between the roller and the guideway, which minimizes wear. Specialized variants such as crossed roller guideways take this a step further by offering four-way equal stiffness, making them the gold standard for ultra-precision tasks such as optical instrument assembly or robotic arm articulation. The main brand series of roller guideways include the THK RGH series, IKO, Schneeberger roller guideways and NSK CRW series.
Key Differences of Linear Ball Guide and Linear Roller Guide:
Factor | Ball Guides | Roller Guides |
Load Capacity | Low-Medium (max. 50–80 kN) | High-Extreme (up to 300+ kN) |
Speed/Acceleration | Higher (up to 100 m/min) | Lower (50–80 m/min) |
Precision | Ultra-high (μm-level) | High (sub-micron with crossed types) |
Durability Under Load | Prone to wear under shock/vibration | Exceptional fatigue resistance |
Cost | Lower | Higher (especially crossed types) |
Selection Guidelines Considerations:
For linear motion, the answer to any question starts with your application. The application and goals determine which solution is best. In other words, the choice between ball and roller depends on what you want to achieve:
Speed & Precision → Ball Guides.
Rigidity & Heavy Loads → Roller Guides.
For expert guidance tailored to your CNC needs, contact RicoCNC.
RicoCNC supplies ball guide and roller guides bearing with different brands: IKO,THK, INA, Rexroth, Hiwin, ABBA, PMI, SBI, etc.
Tel:+86-51268235075
Fax :+86-51268235075
Mobile:+86-13390848665
E-mail: cncsale@ricocnc.com
Skype: ccsalce
Whatsapp: +86-13390848665


